Comprehensive Guide to Shipboard Incineration: Enhancing Safety and Compliance
In the maritime industry, managing waste onboard is critical for both environmental protection and operational safety. Shipboard incineration is one of the primary methods used to dispose of waste generated on ships. Effective operation and maintenance of shipboard incinerators require comprehensive knowledge and adherence to international regulations. This guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of shipboard incineration, covering regulations, waste management, operational requirements, and safety protocols.
Importance of Shipboard Incineration
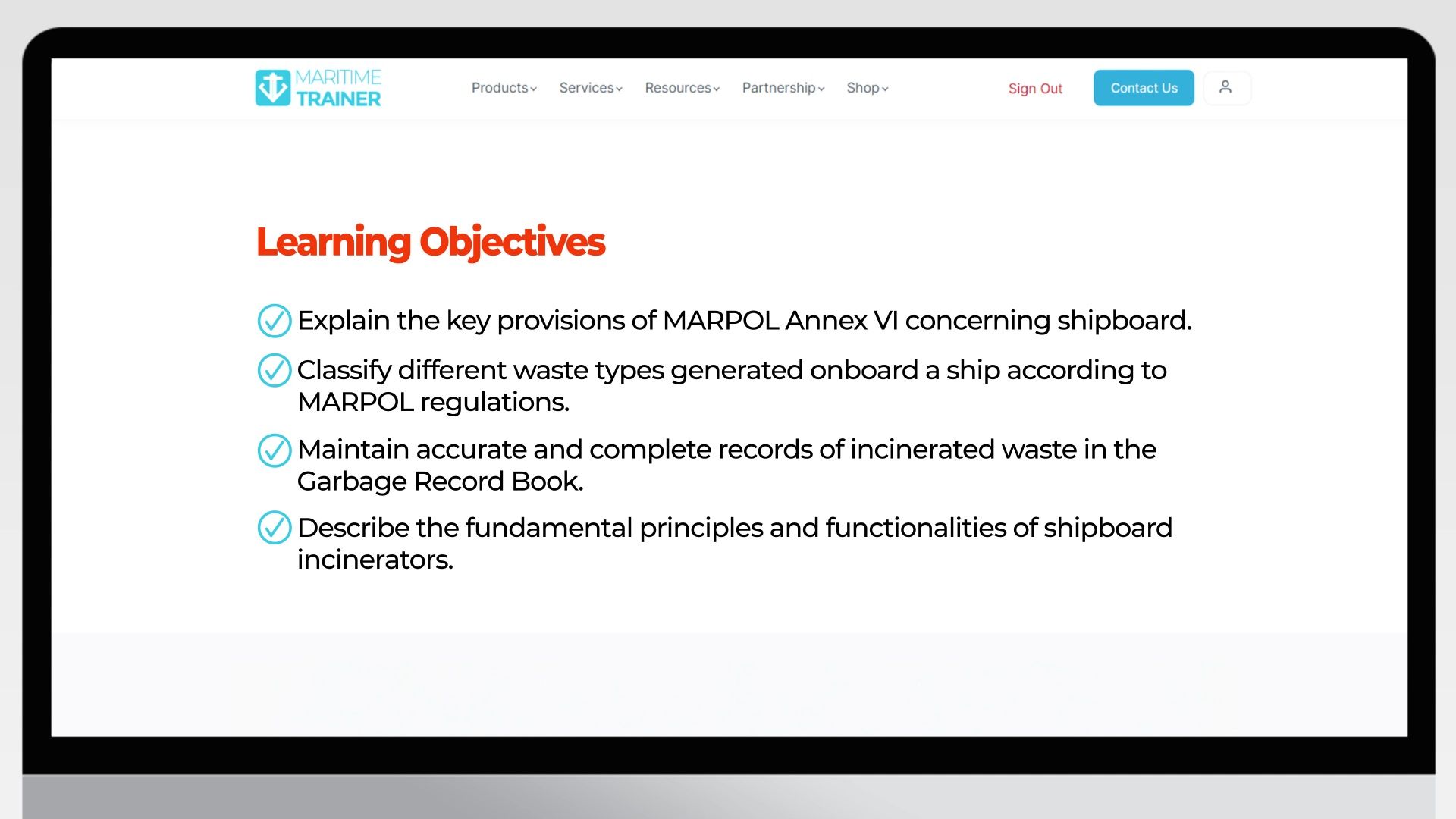
Applicable Regulations
Shipboard incineration is governed by international regulations to ensure safety and environmental protection. The primary regulatory framework is provided by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) through the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution from Ships (MARPOL).

MARPOL Annex VI
- Regulation 16: Specifies the operational requirements for shipboard incinerators, including design, installation, and operation standards.
- MEPC.59(33), MEPC.76(40), and MEPC.244(66): These amendments and guidelines provide detailed instructions on the allowable types of waste for incineration and the performance standards for incinerators.
Compliance with these regulations ensures that shipboard incineration does not contribute to air pollution and that hazardous emissions are minimized.
Types of Marine Incinerators
There are several types of marine incinerators, each designed for specific waste types and operational requirements. The main types include:
- Batch Incinerators: Suitable for small to medium-sized vessels, these incinerators process waste in batches.
- Continuous Feed Incinerators: Used on larger ships, these incinerators allow for continuous waste feed and are more efficient for large volumes of waste.
- Sludge Incinerators: Designed to handle oily waste and sludge, these incinerators are essential for vessels that produce significant amounts of oil residue.
Main Components of Ship Incinerators
- Combustion Chamber: Where the waste is burned at high temperatures.
- Burners: Provide the necessary heat for combustion.
- Flue Gas Treatment System: Removes harmful emissions from the exhaust gases.
- Waste Feed System: Manages the input of waste into the incinerator.
- Ash Removal System: Handles the removal and storage of ash residues.
Operating Requirements as per Regulation 16 of MARPOL
Operating a shipboard incinerator requires strict adherence to the guidelines set out in Regulation 16 of MARPOL Annex VI. Key requirements include:
- Authorized Operation: Incinerators must be operated by trained personnel who are familiar with the equipment and procedures.
- Waste Segregation: Only allowable waste types should be incinerated, and hazardous waste must be managed according to specific guidelines.
- Temperature Control: The combustion chamber must maintain appropriate temperatures to ensure complete combustion and minimize harmful emissions.
- Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of the incinerator and its components are mandatory to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Safety Features

- Automatic Shut-off Systems: In case of malfunction or excessive temperature, the incinerator will automatically shut down to prevent accidents.
- Emission Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of emissions ensures compliance with environmental standards and helps detect any operational issues.
- Safety Interlocks: These prevent the operation of the incinerator if certain safety conditions are not met, such as the presence of unauthorized waste or insufficient ventilation.
Efficient Maintenance Process
- Routine Inspections: Regular checks of the combustion chamber, burners, and flue gas treatment system to identify and address wear and tear.
- Cleaning and Servicing: The combustion chamber and ash removal system are periodically cleaned to prevent buildup and ensure efficient operation.
- Component Replacement: Timely replacement of worn-out or damaged components to maintain the reliability and safety of the incinerator.
Safety of the Operator
Ensuring the safety of operators is a critical aspect of shipboard incineration. Operators must be trained in:
- Safe Handling of Waste: Understanding the proper procedures for handling and feeding waste into the incinerator.
- Emergency Procedures: Knowing how to respond to emergencies, such as fires or equipment malfunctions.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Using appropriate PPE, such as gloves, goggles, and respirators, to protect against exposure to hazardous substances.
Conclusion
Shipboard incineration is an essential process for managing waste on ships, reducing environmental impact, and ensuring the safety of maritime operations. Adherence to international regulations, proper operation and maintenance of incinerators, and comprehensive personnel training are key to achieving these goals. By following best practices and staying updated with regulatory changes, maritime professionals can enhance safety and compliance in shipboard incineration.
Contact us

Approved & Certified by Bureau Veritas

We are proud to be member of


